Suffering from a stress fracture can be a frustrating setback, especially if you're an active individual. However, with the right approach and a well-structured recovery plan, you can overcome this injury and return to your favorite activities stronger than ever. In this blog post, we will explore the essential steps and strategies to help you successfully recover from a stress fracture.
Before diving into the recovery process, it's crucial to understand what a stress fracture is and why it occurs. A stress fracture is a small crack in a bone that results from repetitive stress and overuse. It commonly affects weight-bearing bones such as the shins, feet, and hips. Recognizing the causes and symptoms of stress fractures will aid in your recovery journey.

Seek Professional Medical Evaluation: If you suspect you have a stress fracture, it's essential to consult a medical professional for an accurate diagnosis. A healthcare provider, such as an orthopedic specialist, can conduct physical examinations, imaging tests, and assess your medical history to confirm the presence of a stress fracture. Once diagnosed, they will provide specific guidelines tailored to your situation.
Embrace Rest and Modify Activities: Rest is a critical component of stress fracture recovery. Depending on the severity of the fracture, you may need to immobilize the affected area with a cast, brace, or crutches. It's crucial to follow your healthcare provider's recommendations and avoid any weight-bearing activities or exercises that may delay the recovery of your injury. Consider incorporating low-impact activities, such as swimming or cycling, into your routine to maintain fitness without straining the affected bone.

Implement a Gradual Return-to-Activity Plan: Returning to your regular activities too soon can prolong your recovery or lead to re-injury. Once you receive the green light from your healthcare provider, gradually reintroduce weight-bearing exercises and activities. Start with gentle movements and low-impact exercises, gradually increasing the intensity and duration over time. A physical therapist can guide you through a structured rehabilitation program, ensuring a safe and steady progression.
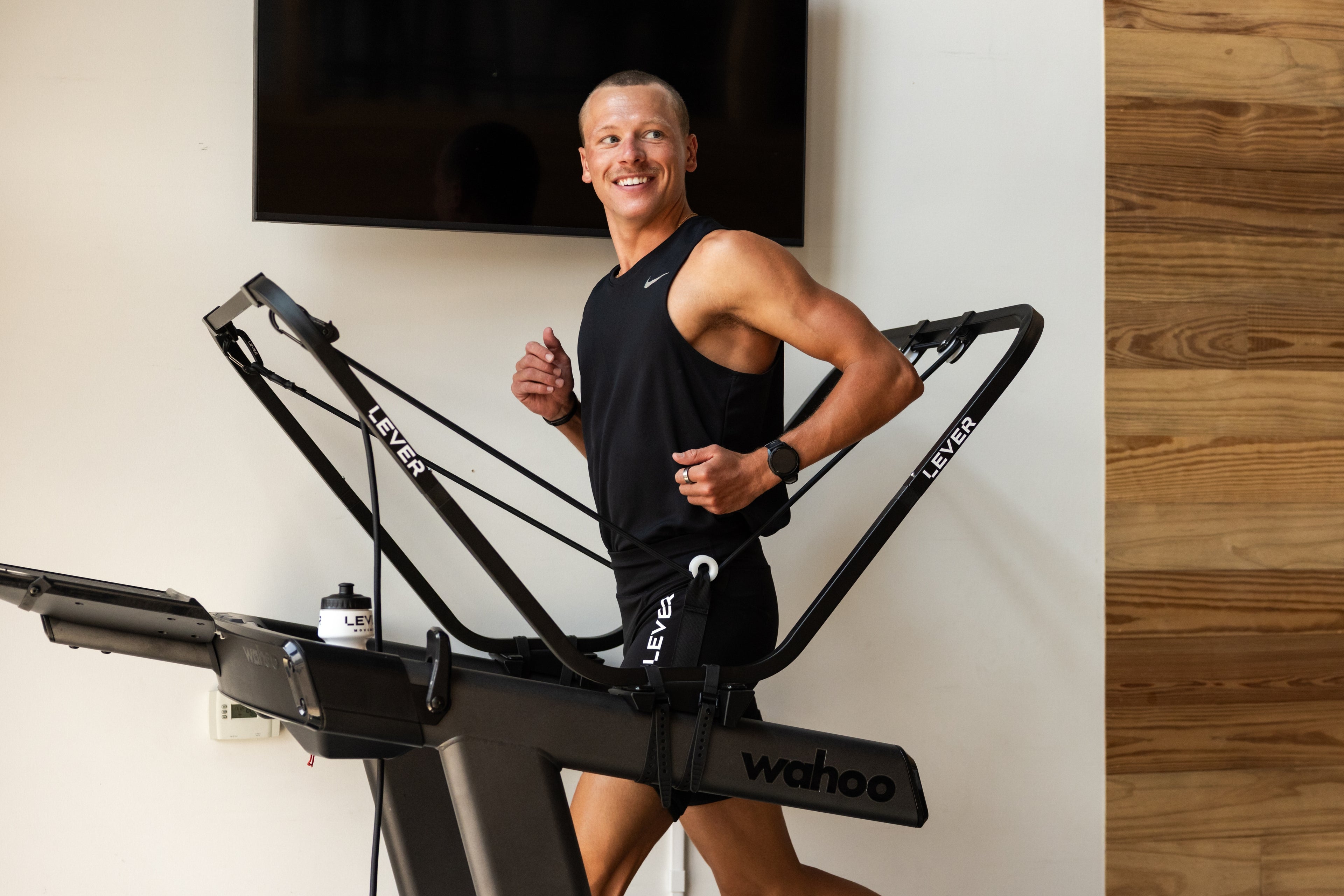
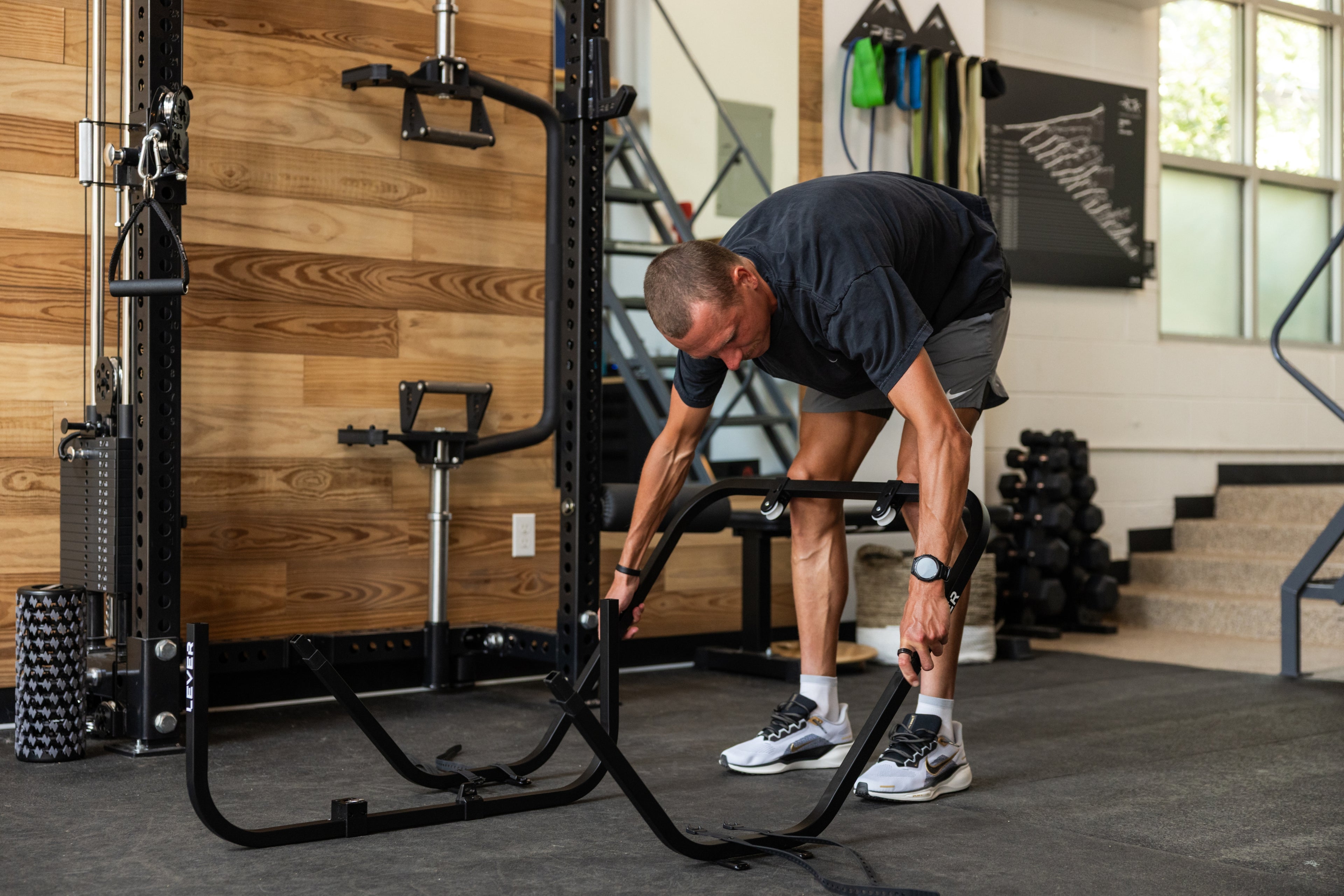
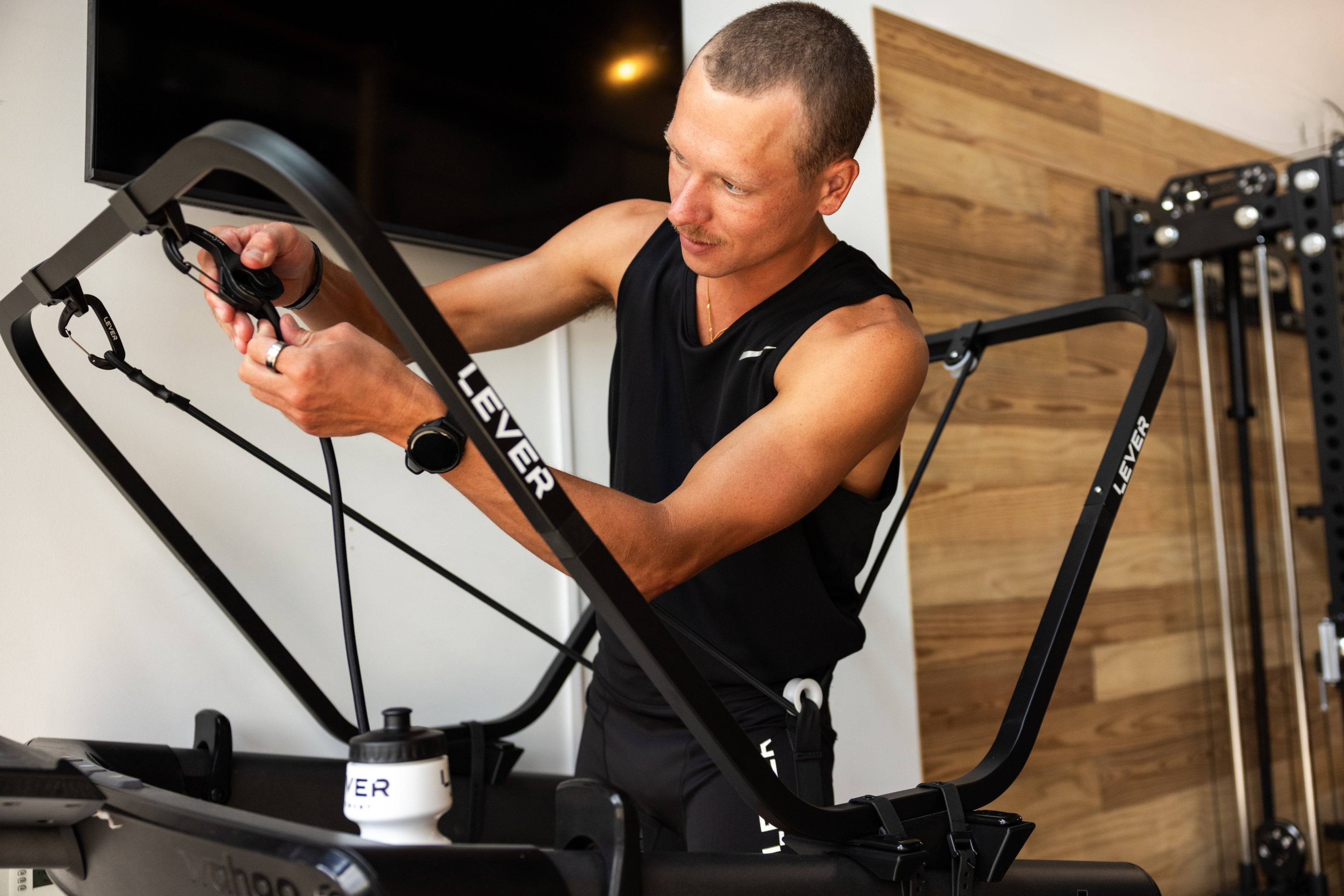
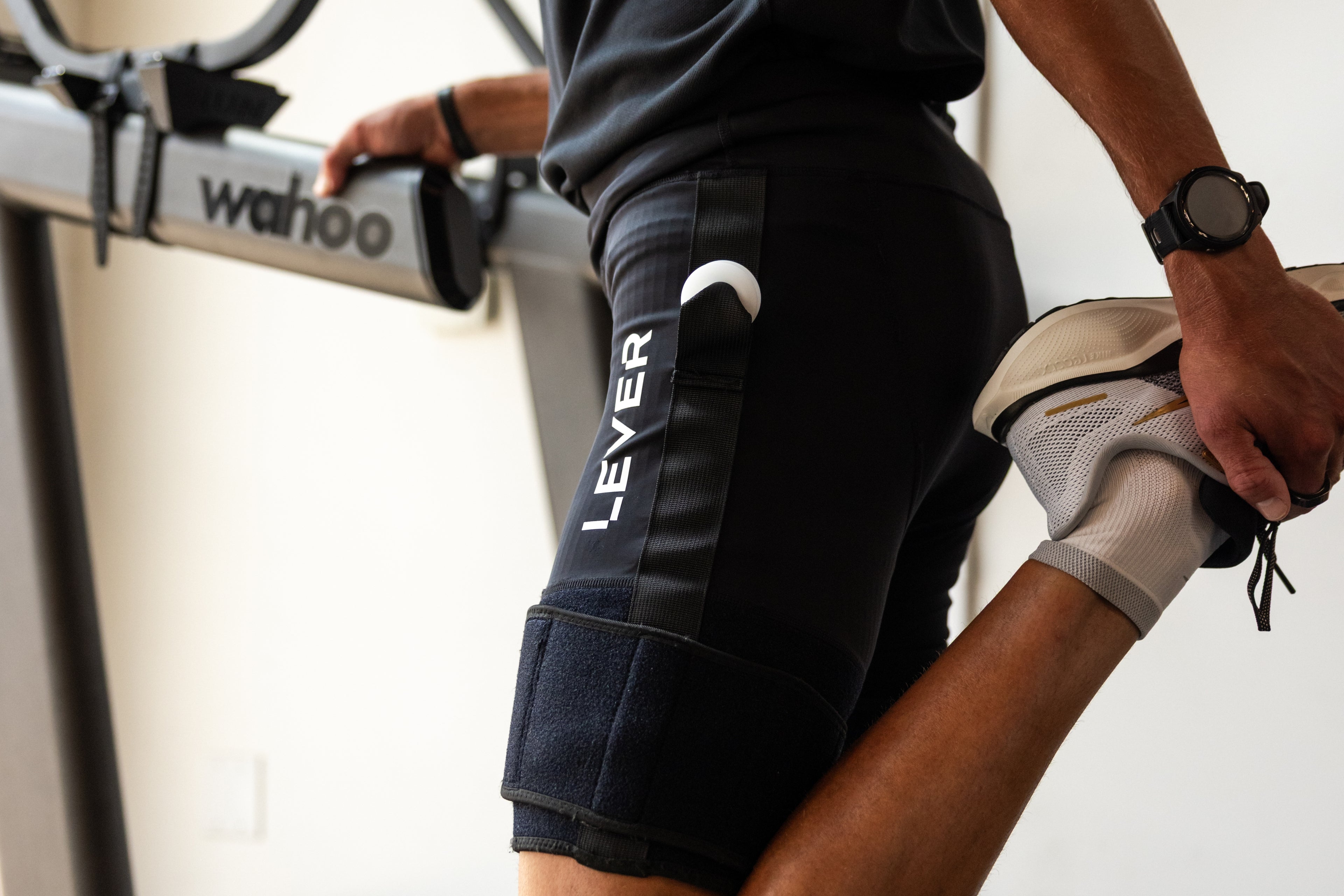
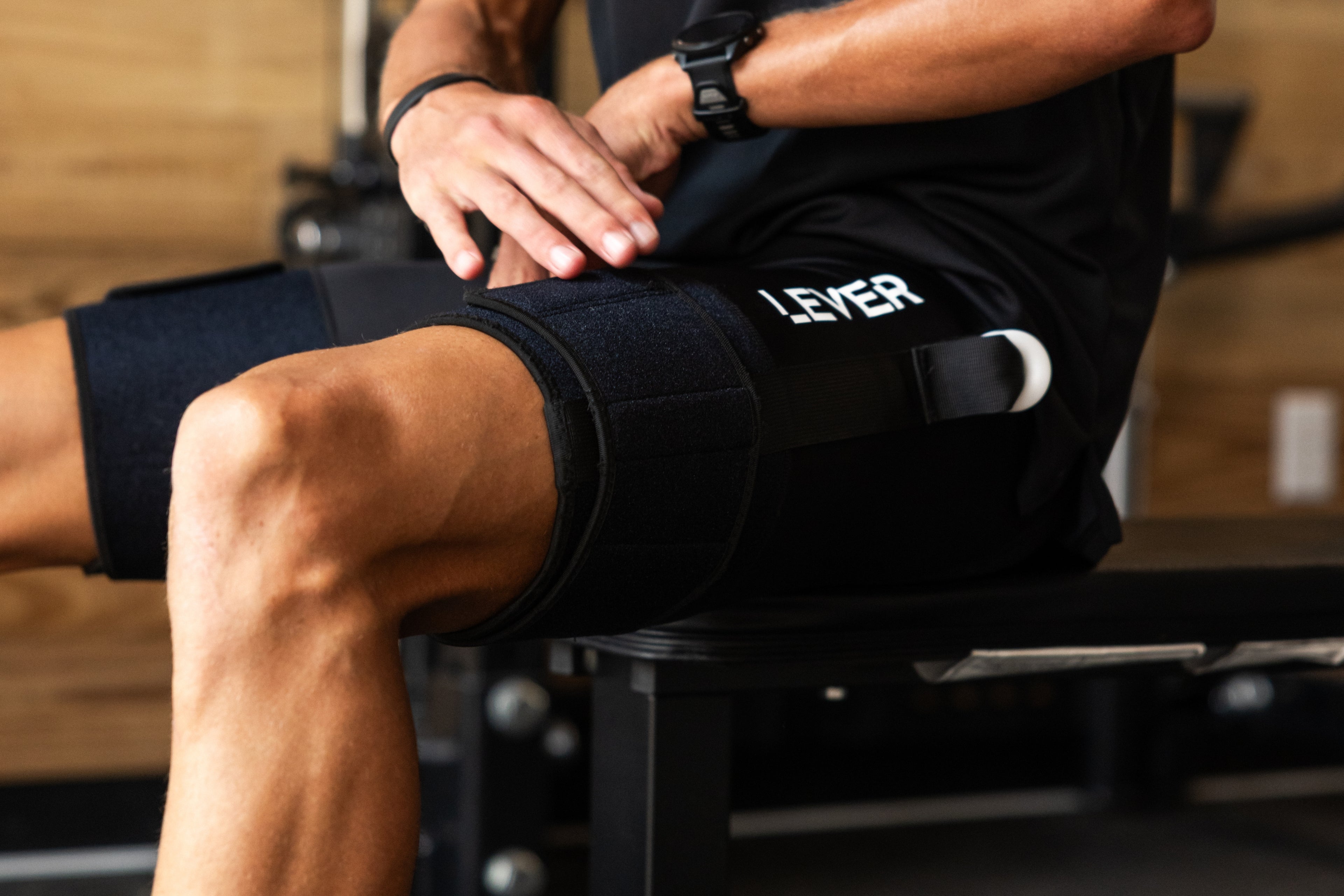
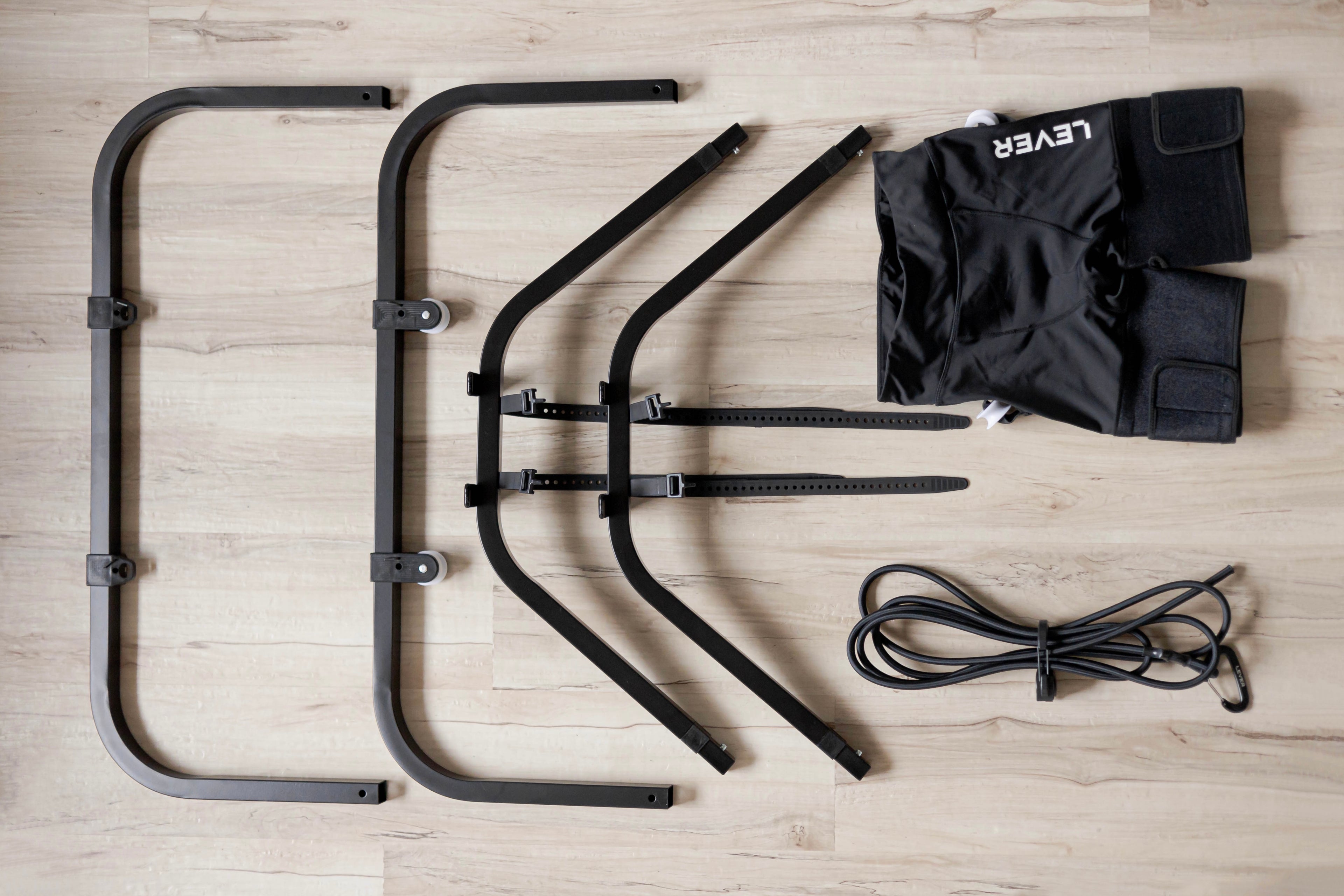
Incorporate Body Weight Support: Incorporating body weight support during the recovery process can be beneficial, especially for lower extremity stress fractures. Techniques such as pool running or using LEVER can help reduce the impact on your bones while allowing you to engage in weight-bearing movements. These methods provide an opportunity to maintain cardiovascular fitness and muscle strength without putting excessive stress on the healing fracture.

Strengthening and Conditioning: As your stress fracture heals, it's crucial to focus on strengthening the surrounding muscles and improving your overall conditioning. Incorporate exercises that target the specific muscle groups supporting the affected area. Gradually increase the load and intensity of your exercises under the guidance of a physical therapist. This will help enhance bone density, improve stability, and reduce the risk of future injuries. Different Types of Stress Fractures and Healing Time: Stress fractures can vary in severity and location, affecting different bones in the body.
Here are a few examples:
Tibia (shin) stress fractures: These are common in runners and athletes involved in high-impact sports. Recovery times can range from 6 to 8 weeks for less severe cases, while more complex fractures may require 3 to 6 months or longer to heal.
Metatarsal stress fractures: Usually occurs in the feet, particularly in the second and third metatarsal bones. Healing time can range from 6 to 8 weeks for minor fractures, but more severe cases may take up to 3 to 4 months.
Navicular stress fractures: Are common in the midfoot and are more challenging to heal due to limited blood supply in the area. Healing times can range from 8 to 12 weeks, with some cases requiring up to 6 months of recovery.
It's important to note that these timeframes are general estimates, and individual healing times can vary. Working closely with your healthcare provider and following their advice will help you better understand the specific healing timeline for your fracture.